The 'value' of a degree
I’ve got two things to say about this article in The Economist. One is to do with alternative credentialing, and the other is to do with my first degree.
- The rhetoric around Open Badges in the early days was that it would mean the end of universities. Instead, they have co-opted them as 'microcredentials' in a way that unbundles chunky degrees into bitesize pieces. Universities are now more likely to work with employers on these microcredentials, which is a benefit to employability, at the expense of a rounded 'liberal' education.
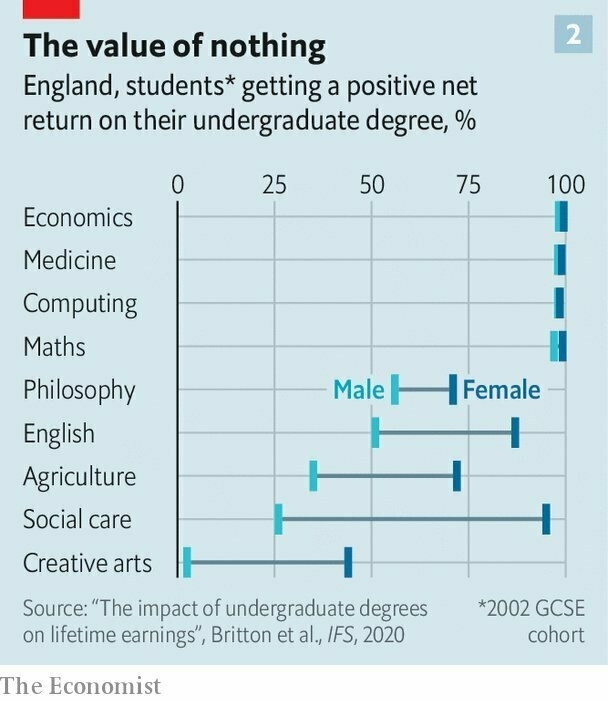
- My first degree was in Philosophy, which most people would assume makes you entirely unemployable. The reverse is actually true, especially for knowledge work. I should imagine that in a world where we need, for example, more AI ethicists, this trend will only continue.
Source: Was your degree really worth it? | The EconomistIn England 25% of male graduates and 15% of female ones will take home less money over their careers than peers who do not get a degree, according to the Institute for Fiscal Studies (IFS), a research outfit. America has less comprehensive data but has begun publishing the share of students at thousands of institutions who do not manage to earn more than the average high-school graduate early on. Six years after enrolment, 27% of students at a typical four-year university fail to do so, calculate researchers at Georgetown University in Washington, dc. In the long tail, comprising the worst 30% of America’s two- and four-year institutions, more than half of people who enroll lag this benchmark.
[…]
Earnings data in Britain call into question the assumption that bright youngsters will necessarily benefit from being pushed towards very selective institutions, says Jack Britton of the ifs. In order to beat fierce competition for places, some youngsters apply for whatever subject seems easiest, even if it is not one that usually brings a high return. Parents fixated on getting their offspring into Oxford or Cambridge, regardless of subject, should take note. But there is also evidence that tackling a high-earning course for the sake of it can backfire. Norwegian research finds that students whose true desire is to study humanities, but who end up studying science, earn less after ten years than they probably otherwise would have.