-
Community forms based off of a common interest, personality, value set, etc. We’ll describe “people who strongly share the interest/personality/value” as Possums: people who like a specific culture. These people have nothing against anybody, they just only feel a strong sense of community from really particular sorts of people, and tend to actively seek out and form niche or cultivated communities. To them, “friendly and welcoming” community is insufficient to give them a sense of belonging, so they have to actively work to create it. Possums tend to (but not always) be the originators of communities.
-
This community becomes successful and fun
-
Community starts attracting Otters: People who like most cultures. They can find a way to get along with anybody, they don’t have specific standards, they are widely tolerant. They’re mostly ok with whatever sort of community comes their way, as long as it’s friendly and welcoming. These Otters see the Possum community and happily enter, delighted to find all these fine lovely folk and their interesting subculture.(e.g., in a christian chatroom, otters would be atheists who want to discuss religion; in a rationality chatroom, it would be members who don’t practice rationality but like talking with rationalists)
-
Community grows to have more and more Otters, as they invite their friends. Communities tend to acquire Otters faster than Possums, because the selectivity of Possums means that only a few of them will gravitate towards the culture, while nearly any Otter will like it. Gradually the community grows diluted until some Otters start entering who don’t share the Possum goals even a little bit – or even start inviting Possum friends with rival goals. (e.g., members who actively dislike rationality practices in the rationality server).
-
Possums realize the community culture is not what it used to be and not what they wanted, so they try to moderate. The mods might just kick and ban those farthest from community culture, but more frequently they’ll try to dampen the blow and subsequent outrage by using a constitution, laws, and removal process, usually involving voting and way too much discussion.
-
The Otters like each other, and kicking an Otter makes all of the other Otters members really unhappy. There are long debates about whether or not what the Possum moderator did was the Right Thing and whether the laws or constitution are working correctly or whether they should split off and form their own chat room
-
The new chat room is formed, usually by Otters. Some of the members join both chats, but the majority are split, as the aforementioned debates generated a lot of hostility
-
Rinse and repeat—
- Wet Plate Photography Makes Tattoos Disappear (PetaPixel) — the photographic technology in the 1800s used to photographic the indigenous Māori people of New Zealand didn't show their facial tattoos.
- Archive shows medieval nun faked her own death to escape convent (The Guardian) — entertaining, but also pretty tragic if you think about the number of young women 'sent away' to convents in the past.
- Why Do People With Depression Like Listening To Sad Music? (The British Psychological Society) — no definitive answers, but seems to back up the commonsense assumption that high-energy music when you're feeling down is just annoying.
- We studied what 10,000 people love online. The results would make Freud blush (Fast Company) — dark nudges, disaster porn, and harder/faster/weirder algorithms.
- The Case for Doing Nothing (The New York Times) — reminiscent of Jocelyn K. Glei's question: "who are you without the doing?"
Offline for 3 days
David Cain took three days offline. It sounds like something that wouldn’t have been amazing 15 years ago, but these days goes straight to the front page of Hacker News.
I can understand why it’s weird to live in the hybrid world of being middle-aged and being alive before everything and everyone was online. But the big thing we need to do is to help the next generations understand that there is an offline world which is rich and worthwhile.
This simplicity was disorienting in a way. Many times a day I would finish whatever activity I was doing, and realize there was nothing to do but consciously choose another activity and then do that. This is how I made my first bombshell discovery: I take out my phone every time I finish doing basically anything, knowing there will be new emails or mentions or some other dopaminergic prize to collect. I have been inserting an open-ended period of pointless dithering after every intentional task.Source: Raptitude.com – Getting Better at Being Human
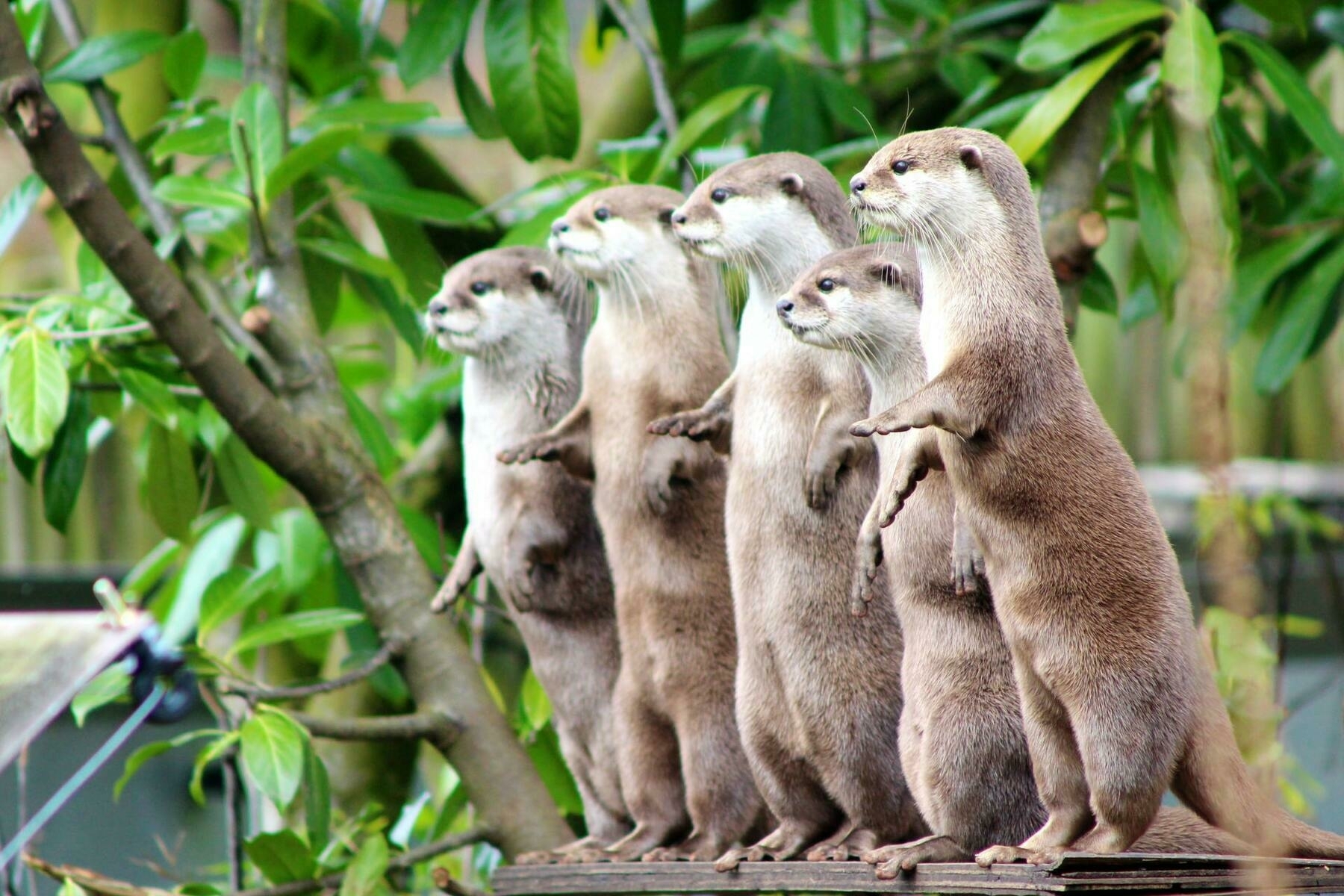
Otters vs. Possums
It’s an odd metaphor, but the behaviours described in terms of internet communities are definitely something I’ve witnessed in 25 years of being online.
(This post is from 2017 but popped up on Hacker News recently.)
There’s a pattern that inevitably emerges, something like this:Source: Internet communities: Otters vs. Possums | knowingless
Like the flight of a sparrow through a lighted hall, from darkness into darkness

⚽ Is it too late to halt football’s final descent into a dystopian digital circus?
🎧 Why Music is Helpful for Concentration
😬 I Lived Through Collapse. America Is Already There.
😷 COVID-19 map for schools (UK)
Quotation-as-title from St Bede. Image from top-linked post.
Fascinating Friday Facts
Here's some links I thought I'd share which struck me as interesting:
Header image: Keep out! The 100m² countries – in pictures (The Guardian)
The security guide as literary genre
I stumbled across this conference presentation from back in January by Jeffrey Monro, “a doctoral student in English at the University of Maryland, College Park, where [he studies] the textual and material histories of media technologies”.
It’s a short, but very interesting one, taking a step back from the current state of play to ask what we’re actually doing as a society.
Over the past year, in an unsurprising response to a host of new geopolitical realities, we’ve seen a cottage industry of security recommendations pop up in venues as varied as The New York Times, Vice, and even Teen Vogue. Together, these recommendations form a standard suite of answers to some of the most messy questions of our digital lives. “How do I stop advertisers from surveilling me?” “How do I protect my internet history from the highest bidder?” And “how do I protect my privacy in the face of an invasive or authoritarian government?”It's all very well having a plethora of guides to secure ourselves against digital adversaries, but this isn't something that we need to really think about in a physical setting within the developed world. When I pop down to the shops, I don't think about the route I take in case someone robs me at gunpoint.
So Monro is thinking about these security guides as a kind of ‘literary genre’:
I’m less interested in whether or not these tools are effective as such. Rather, I want to ask how these tools in particular orient us toward digital space, engage imaginaries of privacy and security, and structure relationships between users, hackers, governments, infrastructures, or machines themselves? In short: what are we asking for when we construe security as a browser plugin?There's a wider issue here about the pace of digital interactions, security theatre, and most of us getting news from an industry hyper-focused on online advertising. A recent article in the New York Times was thought-provoking in that sense, comparing what it's like going back to (or in some cases, getting for the first time) all of your news from print media.
We live in a digital world where everyone’s seemingly agitated and angry, all of the time:
The increasing popularity of these guides evinces a watchful anxiety permeating even the most benign of online interactions, a paranoia that emerges from an epistemological collapse of the categories of “private” and “public.” These guides offer a way through the wilderness, techniques by which users can harden that private/public boundary.The problem with this 'genre' of security guide, says Monro, is that even the good ones from groups like EFF (of which I'm a member) make you feel like locking down everything. The problem with that, of course, is that it's very limiting.
Communication, by its very nature, demands some dimension of insecurity, some material vector for possible attack. Communication is always already a vulnerable act. The perfectly secure machine, as Chun notes, would be unusable: it would cease to be a computer at all. We can then only ever approach security asymptotically, always leaving avenues for attack, for it is precisely through those avenues that communication occurs.I'm a great believer in serendipity, but the problem with that from a technical point of view is that it increases my attack surface. It's a source of tension that I actually feel most days.
There is no room, or at least less room, in a world of locked-down browsers, encrypted messaging apps, and verified communication for qualities like serendipity or chance encounters. Certainly in a world chock-full with bad actors, I am not arguing for less security, particularly for those of us most vulnerable to attack online... But I have to wonder how our intensive speculative energies, so far directed toward all possibility for attack, might be put to use in imagining a digital world that sees vulnerability as a value.At the end of the day, this kind of article serves to show just how different our online, digital environment is from our physical reality. It's a fascinating sideways look, looking at the security guide as a 'genre'. A recommended read in its entirety — and I really like the look of his blog!
Source: Jeffrey Moro