Conversational affordances
I’m one of those people who has to try hard not to over-analyse everything. Therapy has helped a bit, but I still can’t help reflecting on conversations I’ve had with people outside my family.
Why did that conversation go so well? Why was another one boring? Did I talk too much?
That sort of thing.
Which is why I found this article about ‘conversational doorknobs’ and improvisational comedy fascinating.
For me, learning take-and-take suggested a solution not just to songs about Spiderman, but to a scientific mystery. I was in graduate school at the time, running studies aimed at answering the question, “Do conversations end when people want them to?” I watched a stupefying number of conversations unfold, some of them blooming into beautiful repartee (one pair of participants exchanged numbers afterward), others collapsing into awkward silences. Why did some conversations unfurl and others wilt? One answer, I realized, may be the clash of take-and-take vs. give-and-take.There’s people I interact with on a semi-regular basis for which I, like other people, am just a convenient person to talk at. It can be entertaining for a while, but can get a bit too much. Likewise, there are others where I feel like I have to do most of the talking, and that’s just tiring.Givers think that conversations unfold as a series of invitations; takers think conversations unfold as a series of declarations. When giver meets giver or taker meets taker, all is well. When giver meets taker, however, giver gives, taker takes, and giver gets resentful (“Why won’t he ask me a single question?”) while taker has a lovely time (“She must really think I’m interesting!”) or gets annoyed (“My job is so boring, why does she keep asking me about it?”).
It’s easy to assume that givers are virtuous and takers are villainous, but that’s giver propaganda. Conversations, like improv scenes, start to sink if they sit still. Takers can paddle for both sides, relieving their partners of the duty to generate the next thing. It’s easy to remember how lonely it feels when a taker refuses to cede the spotlight to you, but easy to forget how lovely it feels when you don’t want the spotlight and a taker lets you recline on the mezzanine while they fill the stage. When you’re tired or shy or anxious or bored, there’s nothing better than hopping on the back of a conversational motorcycle, wrapping your arms around your partner’s waist, and holding on for dear life while they rocket you to somewhere new.
The best thing is when the two of your have a shared interest and you’re willing to take turns in asking questions and opening doorways. I’m not saying that I’m a particularly skilled conversationalist, but having attended a lot of events during my career, I’m better at it now than I used to be.
When done well, both giving and taking create what psychologists call affordances: features of the environment that allow you to do something. Physical affordances are things like stairs and handles and benches. Conversational affordances are things like digressions and confessions and bold claims that beg for a rejoinder. Talking to another person is like rock climbing, except you are my rock wall and I am yours. If you reach up, I can grab onto your hand, and we can both hoist ourselves skyward. Maybe that’s why a really good conversation feels a little bit like floating.Source: Good conversations have lots of doorknobs | Experimental HistoryWhat matters most, then, is not how much we give or take, but whether we offer and accept affordances. Takers can present big, graspable doorknobs (“I get kinda creeped out when couples treat their dogs like babies”) or not (“Let me tell you about the plot of the movie ‘Must Love Dogs’…”). Good taking makes the other side want to take too (“I know! My friends asked me to be the godparent to their Schnauzer, it’s so crazy” “What?? Was there a ceremony?”). Similarly, some questions have doorknobs (“Why do you think you and your brother turned out so different?”) and some don’t (“How many of your grandparents are still living?”). But even affordance-less giving can be met with affordance-ful taking (“I have one grandma still alive, and I think a lot about all this knowledge she has––how to raise a family, how to cope with tragedy, how to make chocolate zucchini bread––and how I feel anxious about learning from her while I still can”).
[…]
A few unfortunate psychological biases hold us back from creating these conversational doorknobs and from grabbing them when we see them. We think people want to hear about exciting stuff we did without them (“I went to Budapest!”) when they actually are happier talking about mundane stuff we did together (“Remember when we got stuck in traffic driving to DC?”). We overestimate the awkwardness of deep talk and so we stick to the boring, affordance-less shallows. Conversational affordances often require saying something at least a little bit intimate about yourself, so even the faintest fear of rejection on either side can prevent conversations from taking off. That’s why when psychologists want to jump-start friendship in the lab, they have participants answer a series of questions that require steadily escalating amounts of self-disclosure (you may have seen this as “The 36 Questions that Lead to Love”).
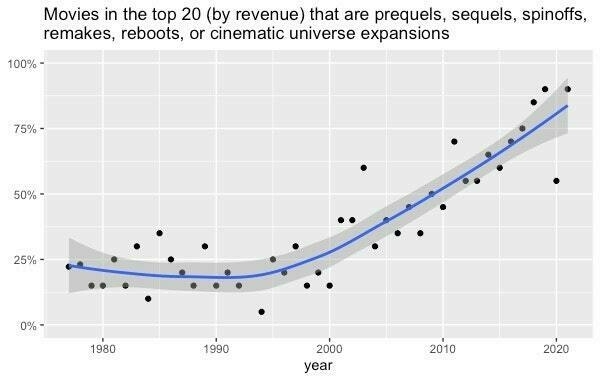
Popular culture has become an endless parade of sequels
Once you start recognising colour schemes and sound effects, every new film ends up looking and sounding the same.
Yes, I’m getting old, but as Adam Mastroianni from Experimental History explains, there’s shifts happening in everything from books to video games.
The problem isn’t that the mean has decreased. It’s that the variance has shrunk. Movies, TV, music, books, and video games should expand our consciousness, jumpstart our imaginations, and introduce us to new worlds and stories and feelings. They should alienate us sometimes, or make us mad, or make us think. But they can’t do any of that if they only feed us sequels and spinoffs. It’s like eating macaroni and cheese every single night forever: it may be comfortable, but eventually you’re going to get scurvy.Source: Pop Culture Has Become an Oligopoly | Experimental History[…]
Fortunately, there’s a cure for our cultural anemia. While the top of the charts has been oligopolized, the bottom remains a vibrant anarchy. There are weird books and funky movies and bangers from across the sea. Two of the most interesting video games of the past decade put you in the role of an immigration officer and an insurance claims adjuster. Every strange thing, wonderful and terrible, is available to you, but they’ll die out if you don’t nourish them with your attention. Finding them takes some foraging and digging, and then you’ll have to stomach some very odd, unfamiliar flavors. That’s good. Learning to like unfamiliar things is one of the noblest human pursuits; it builds our empathy for unfamiliar people. And it kindles that delicate, precious fire inside us––without it, we might as well be algorithms. Humankind does not live on bread alone, nor can our spirits long survive on a diet of reruns.